The Best TV Buying Guide

The Era of Overspecification! Which TV Should You Buy?
TVs come in a wide variety of types, and new technologies are being rapidly developed. Prices range from as low as $225 to tens of thousands of dollars. While high-end, high-performance products are equipped with excellent technology, they may be overspecified for general home TV viewing purposes.
I’ll guide you on how to choose a TV based on the needs of users who watch regular TV or OTT broadcasts at home, rather than those who use it for high-spec gaming or viewing high-quality videos. This will help you find the TV that’s right for you.
Chapter 1.
TV Picture Quality
Operating Method (Panel) / Resolution / Contrast Ratio
1. Operating Method (Panel/Backlight)
OLED > Mini LED > Nanocell/QLED > LED
Considering cost-effectiveness, LED also provides sufficient picture quality
Picture quality is the most important factor when choosing a TV. Better picture quality allows for brighter and clearer viewing. The operating method (panel/backlight), resolution, TV size, and contrast ratio have the most significant impact on picture quality. Let’s first look at the operating method.
Most TVs Today are LED TVs

The evolution of TV technology has progressed from the bulky CRT TVs → PDPs that popularized large TVs → LCDs that improved picture quality → LEDs with thinner profiles due to LED backlights → OLEDs. Recently, products that maximize contrast ratio, which was the main drawback of LED TVs, by incorporating Mini LED backlight technology in LCD panels are gradually being released. These are positioned between LED TVs and OLED TVs. Currently, LED TVs have the highest sales volume, but the prices of high-end products with OLED and Mini LED backlights have gradually decreased, making them worth considering for purchase.
Broadly Categorized into OLED and LCD Based on Panel and Light Source

The operating method of TVs differs according to the technology of the panel (screen) and backlight (light source). First, they are divided into OLED and LCD based on the type of light source. Except for self-emitting OLEDs, all use LED backlights in the LCD method. LCDs are further divided into:
1) Regular LED with standard backlight
2) QLED/Nanocell with special coating or film on the panel surface to enhance color
3) Neo QLED/QNED with Mini LED backlight used together with specially coated or filmed panels to enhance both color and contrast ratio
(Regular LCD TVs using CCFL as a light source are rarely sold now.)
Note: QLED (Quantum dot Light Emitting Diode) is a technology that, like OLED, doesn’t require a separate light source and hasn’t been commercialized yet. However, Samsung uses the term QLED TV for marketing its LED TVs with quantum dot panels (QD-LCD).
Cost-Effective LED TVs
LED TVs use LCD panels with LED backlight. While they lack in color reproduction and contrast ratio compared to OLED, they are currently the most basic type.
They provide sufficient picture quality for general TV viewing, making them the most recommended type if you’re considering cost-effectiveness. Samsung’s Crystal UHD and LG’s Ultra HD are examples of this type.
Nanocell and QLED are Evolved LEDs
Nanocell and QLED TV (QD-LCD), which are a step further evolved, use the same LED backlight method but differ in that:
1) LG Nanocell: Applies 1nm-sized ultra-fine molecules to the panel
2) Samsung QLED: Inserts a quantum dot sheet between the backlight and panel
These methods improve picture quality by enhancing color reproduction, brightness, and viewing angle compared to regular LEDs.
QNED/Neo QLED with Improved Contrast Ratio Using Mini LED
LG’s QNED TV and Samsung’s Neo QLED TV are products that improve contrast ratio by using specially treated panels and Mini LEDs, similar to existing Nanocell/QLED TVs (QD-LCD).
1) LG QNED: Uses Nanocell + Quantum Dot technology together to enhance color expression ability, and uses Mini LED to improve contrast ratio
2) Samsung Neo QLED: Applies Mini LED to existing QLED (QD-LCD) panels to improve contrast ratio
Note: The 2022 models of LG QNED TV 80 / 7S line use regular LED as backlight, so you can’t expect the high contrast ratio of products with Mini LED mentioned earlier.
Latest Technology with Best Picture Quality: OLED
Expensive Price and Burn-in are Drawbacks

OLED TVs can be said to have the best picture quality currently available, for these reasons:
1) Very thin profile: The panel emits light on its own, so LED backlight is not needed
2) Very high contrast ratio: Can express perfect black by completely turning off LED elements in dark parts of content 3) Excellent viewing angle: No color difference when viewed from various directions
However, due to the way it emits light and the characteristics of the elements, there are drawbacks such as ‘burn-in’ phenomenon where colors are not properly expressed and marks remain after long use, and the price is at least $750 more expensive compared to LCD.
(OLED TV manufacturers have incorporated an automatic brightness control function called ABL (Auto Brightness Limiter) to prevent burn-in, but some say that this function causes a sense of discomfort as brightness is automatically adjusted when the scene changes (dark scene -> bright scene).)
Choose Considering Sensitivity to Picture Quality and Price
1) If you want the highest level of picture quality and don’t mind the price, choose OLED
2) If OLED is too expensive, but you’re looking for a TV with clear colors and high contrast ratio, choose QNED/Neo QLED
3) If you want higher picture quality than regular LED but high prices are burdensome, choose Nanocell or QLED
4) If you’re not particularly sensitive to picture quality differences and want a large TV, we recommend cost-effective LED TV
If possible, it’s best to experience the picture quality difference with your own eyes at a store before purchasing. However, keep in mind that stores often play video content that maximizes the picture quality of high-spec TVs, which may differ from the environment of general TV broadcasts.
2. TV Resolution
Most recently released TVs are 4K UHD products
Purchasing 8K UHD may be premature
Higher Resolution Means More Pixels
The image you see on a TV is composed of countless tiny dots, each called a pixel. Resolution refers to how many pixels make up an image, with more pixels resulting in a higher-quality image.
4K UHD < 8K UHD

Pixel count is defined as the product of horizontal and vertical pixel numbers. Currently, most TVs on the market have two main resolution types:
1) 4K UHD: 3840 x 2160
2) 8K UHD: 7680 x 4320
8K UHD TVs have four times the number of pixels compared to 4K UHD TVs, making them that much clearer and allowing you to view content on larger screens without pixelation.
| – | 4K UHD | 8K UHD |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal pixels | 3840 | 7680 |
| Vertical pixels | 2160 | 4320 |
| Total pixels | About 8 million | About 33 million |
| Display format | 2160p | 4320p |
| Price range | Starting from about $800 | Starting from about $4,000 |
The ‘K’ in 4K and 8K stands for Kilo, meaning 1000. TVs are called 4K or 8K based on their horizontal pixel count being around 4000 or 8000, respectively. Conversely, they may also be labeled as 2160P for 4K or 4320P for 8K, based on vertical pixel count.
Currently, FHD resolution products are being phased out, with most manufacturers releasing 4K TVs, and 8K TV releases are gradually increasing.
Upscaling Function to Enhance Resolution of Lower-Resolution Content
The Perceptible Effect is Gradually Increasing

Upscaling is a function that converts low-quality FHD content to high-quality 4K or 8K. As it’s a post-processing function to increase resolution, it had technical limitations and wasn’t very noticeable.
However, recent developments in AI-based upscaling technology have made it more effective in correcting noise, texture, and jagged edges, allowing for expectation of higher quality content.
3. HDR (High Dynamic Range)
We recommend TVs with HDR functionality
HDR Allows Viewing That’s Closest to What We See in Reality

Another factor determining picture quality is contrast ratio. Contrast ratio refers to the difference between the minimum and maximum brightness that a screen can display.
The higher the contrast ratio, the darker the dark areas and the brighter the bright areas, resulting in rich color expression that’s similar to what we see with our eyes.
Note: The image above exaggerates the difference and may not reflect the actual difference.
The Importance of HDR Functionality is Growing Beyond Resolution
While manufacturers previously focused on panels and resolution, they’re now putting effort into HDR-related technologies.
HDR (High Dynamic Range) is a specification that can express more delicate brightness than SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) used in current general broadcasts and videos.
To Properly Enjoy HDR, Check if the HDR Type of Your Main Content Provider Matches That of Your TV
Unlike the early days when HDR standards were chaotic, HDR technology is now maturing, with HDR10+ and Dolby Vision becoming the standards. To properly enjoy HDR’s color expression, you need to check if the content provider’s standard matches the HDR type supported by your TV.
For example, if you want to watch Netflix’s HDR content, you need to use a TV that supports HDR10 or Dolby Vision, which are the HDR types supported by Netflix.

Various OTT services like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ are showcasing a lot of HDR-produced content, so it’s good to check what HDR type your main OTT service supports before purchasing a TV.
If You Want to Properly Enjoy HDR Content
Check for DolbyVision / HDR10+ Support

There are various HDR formats including HDR10, HLG, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and Dolby Vision IQ, each with slightly different characteristics:
1) HDR10: Has better color expression ability compared to regular video (SDR), but as it’s an early HDR format, it has limitations when showing diverse backgrounds (bright explosion scenes / dark interiors)
2) HLG: Format used when broadcasting HDR content in live broadcasts or by major broadcasters
3) HDR10+ / Dolby Vision: More evolved HDR formats compared to HDR10, showing optimal brightness and color expression for each background (bright scenes / dark scenes), allowing for more realistic and rich visual beauty
Note: Technicolor is a trend that’s gradually decreasing in brands that incorporate it.
Most recently released TVs support HDR10 / HLG formats as standard, which is sufficient for enjoying HDR content. If you want to choose a TV with even better picture quality and immersion, we recommend choosing a product equipped with HDR10+ / Dolby Vision.
4. Refresh Rate
60Hz is sufficient for general TV viewing
120Hz products are better for gaming/sports content
Refresh Rate Determines Smooth Picture Display

Refresh rate refers to how many images a TV can display per second, measured in Hz (Hertz). The video we see is actually composed of a series of still images (frames).
If a TV’s refresh rate is lower than the frame rate of the video, it can’t show all the frames in a short time, resulting in unnatural playback. Most video content is shot and played at 60 frames per second, so 60Hz is sufficient for enjoying most movies and dramas.
120Hz or Higher Products Are Smoother for Gaming/Sports Content
If you enjoy console games (XBOX/PlayStation) or sports content, we recommend considering 120Hz products. The latest console gaming systems can output at 120Hz high refresh rate in 4K UHD resolution, allowing you to enjoy games with smoother visuals.

Sports broadcasts are content where you can really feel the difference with higher refresh rates. Even if sports content with frequent dynamic scene changes is produced at 60 frames, you can watch it more smoothly and vividly by utilizing the frame interpolation (MEMC) function built into the TV.
(Frame interpolation: A function that virtually creates missing frames to allow for smoother viewing)
When Buying High Refresh Rate TVs from Smaller Companies,
Be Sure to Check HDMI Version and Bandwidth
| – | FHD (1920×1080) | QHD (2560×1440) | 4K UHD (3840×2160) | 5K UHD (5120×2880) | 8K UHD (7680×4320) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI 1.4 | 144Hz | 75Hz | 30Hz | – | – |
| HDMI 2.0 | 240Hz | 144Hz | 60Hz | 30Hz | – |
| HDMI 2.1 (18Gbps) | 240Hz | 144Hz | 60Hz | 30Hz | – |
| HDMI 2.1 (48Gbps) | 240Hz | 240Hz | 144Hz | 60Hz | 30Hz |
When purchasing a high refresh rate TV, you should check both the HDMI version and bandwidth. For 4K, 120Hz, you need to buy a product that supports HDMI 2.1 or higher.
The important point is that while HDMI 2.1 supports a maximum bandwidth of 48Gbps, which in principle allows viewing 4K UHD high-resolution video at 120Hz, some products may be labeled as HDMI 2.1 but have lower bandwidth (18Gbps), resulting in improper video output.
If the main use of your TV is high-resolution, high refresh rate gaming, it’s good to check the bandwidth as well.
Chapter 2.
TV Size
Choosing the Right TV Size Based on Resolution and Viewing Distance
As technology advances, the size of home TVs is getting larger. In the past, there was a saying that “the appropriate TV size is 1.5 times the square footage of your home.”
However, with improvements in TV resolution and picture quality, now people often say “the bigger the TV, the better” or “bigger is always better.” Let’s explore how to choose the right TV size and what size is appropriate for your home.
1. TV Size Notation
TV size is indicated by the diagonal length in inches

While TV size is conceptually the area of the screen (width multiplied by height), the standard unit is the diagonal length in inches. The commonly mentioned 55-inch or 65-inch refers to the diagonal length converted to inches.

Most home TVs currently on sale range from 43 to 85 inches.
2. Choosing Based on Resolution
The higher the resolution, the more effective it is to buy a larger TV
Consider Both Home Size and Resolution
While people usually try to choose TV size based on their home’s square footage or viewing distance, you should first check the resolution of the TV you’re planning to buy. TV size is a factor that can effectively display high-resolution video, so the higher the resolution, the better it is to buy a larger TV.
The resolutions of TVs mainly sold are 4K UHD and 8K UHD, with the larger number before ‘K’ indicating higher resolution.
(Currently, large TVs of 65 inches or more with 2K FHD resolution are rarely released, and can only be found occasionally in small TVs of 50 inches or less. Sales volume is also very low.)
It’s Difficult to Notice the Difference with High Resolution on a Small Screen
For example, if you buy a TV with 4K UHD high resolution but the size is too small, you won’t be able to notice the difference from 2K FHD quality. Conversely, if the resolution is FHD but the TV size is too large, the screen may appear pixelated.
In other words, if you’re buying a high-resolution TV, it’s good to choose a TV that’s correspondingly large. As a rough guideline, for a viewing distance of about 6.5 feet (2m) and 4K resolution, a 65-inch or larger TV won’t appear pixelated.
3. Choosing Based on Viewing Distance
For viewing distances over 6.5 feet (2m), we recommend 65 inches or larger
Match to Viewing Distance, Not Home Size

People usually try to choose a TV based on their home’s square footage. While this isn’t entirely wrong, even homes of the same size can have different living room sizes, and viewing distance can vary depending on the presence and location of a sofa.
Also, if you’re placing the TV in a room other than the living room, it’s more accurate to match it to the viewing distance.
Is “Bigger Always Better” for TVs?
It’s not wrong to say that bigger is better for TVs. There are many reviews saying that while they were initially worried about a 65-inch TV being too big for their 700 sq ft (65 sq m) apartment, their eyes adjusted within 3-4 days and they felt it could be even bigger.

Until just 1-2 years ago, 65 inches could be considered the standard for 4K UHD TVs, but recently 75-inch products are also being sold at affordable prices, widening the range of size choices.
However, from 75 inches and up, the price increase is significant, so we recommend considering the size according to your budget and situation.
However, There is a Maximum Limit for Short Viewing Distances
There is a maximum limit, so if you place an excessively large TV in a space with a short viewing distance, you may see pixelation because you’re viewing the screen too closely, actually decreasing the perceived picture quality. It’s the same principle as when a phone photo looks pixelated if you zoom in too much.
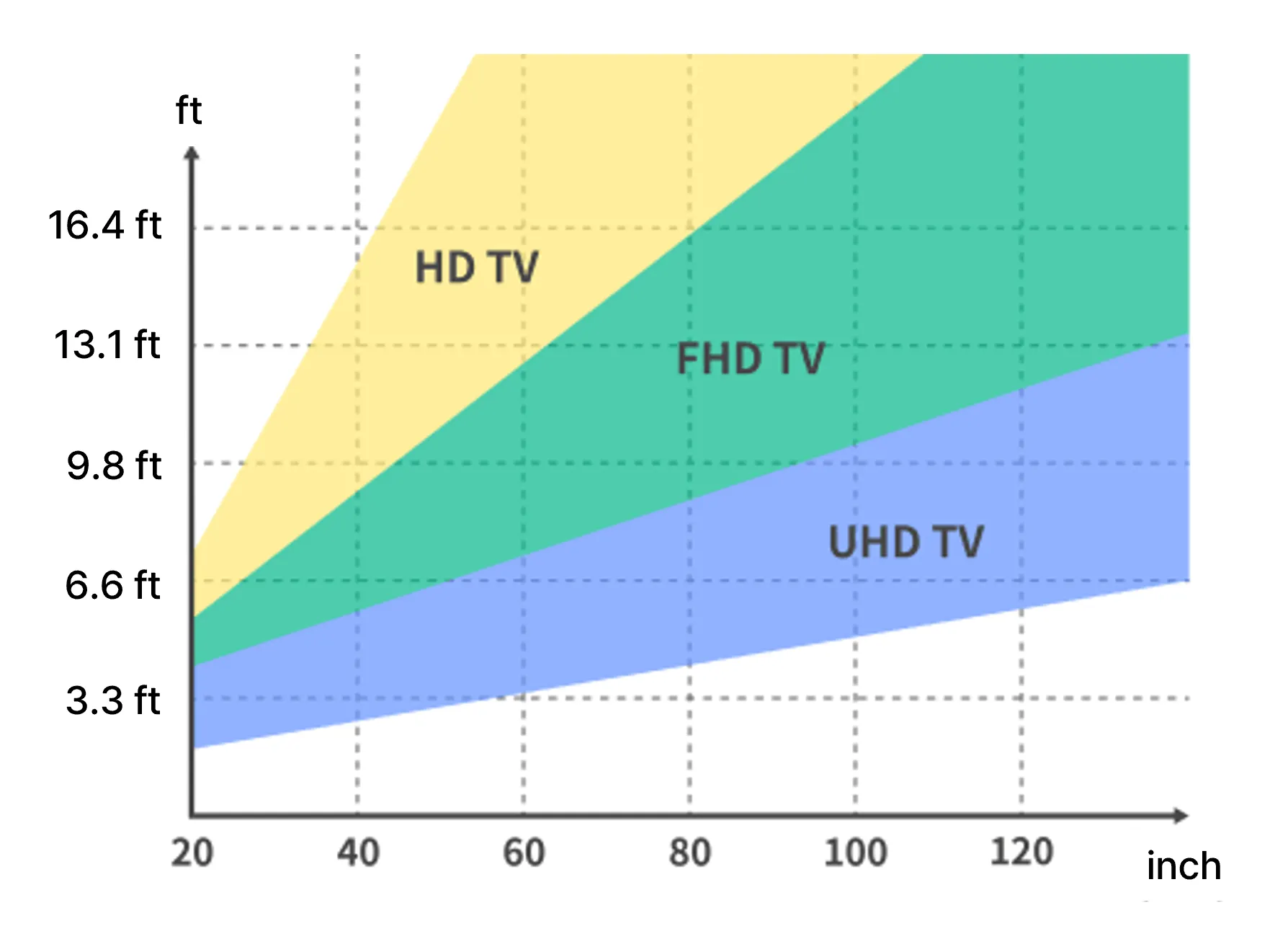
The graph above shows the theoretical viewing distance-screen size for each resolution, based on a person with 20/20 vision. However, considering that most TVs currently sold are less than 80 inches and there isn’t much UHD content yet, it’s best to use this as a reference.
Chapter 3.
TV Additional Features
Sound / Smart Features / Power Consumption
1. Sound
Sound performance isn’t a crucial factor when choosing a TV.
If you’re sensitive to sound quality, we recommend purchasing a separate soundbar.
Higher Number of Sound Channels Provides More Immersive Sound

TV sound is indicated by channels and output. Channels are denoted as 2.1, 4.1, 4.2, etc., where the number before the decimal point represents regular speakers, and the number after represents subwoofers for bass.
Sound Output is a Consideration, Not a Major Purchase Factor

Output is measured in watts (W), and higher output allows for louder sound without noise.
However, built-in TV speakers often direct sound towards the bottom or back of the TV rather than towards the viewer due to the thin profile of modern TVs. As a result, they often have inferior sound quality compared to external speakers with the same output.
We Recommend Purchasing a Separate Soundbar Rather Than Prioritizing TV Sound Performance
While TV sound is improving, it’s slower compared to picture quality improvements. Manufacturers are focusing on making thinner TVs, making it difficult to secure space for speakers to perform optimally.
Therefore, if you want sufficient sound quality to match a high-end TV, we recommend purchasing a separate soundbar rather than focusing on the built-in sound specifications.
2. Smart / Additional Features
There’s no need to buy expensive products just for smart/additional features
Choose Minimally Based on Your Usage Environment
| Feature | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Smart TV | Ability to install and use smart applications |
| Wi-Fi | Can connect to Wi-Fi networks without additional equipment, allowing use of TV web browsers or OTT services |
| Bluetooth | Supports Bluetooth, enabling connection to Bluetooth speakers or smartphones |
| Mirroring | Ability to display smartphone or tablet screens on the TV |
| Voice Recognition (ThinQ AI/Bixby/Google Assistant) | Can control TV functions by voice and search for information |
| SmartThings (IoT/Smart Home Hub) | Ability for the TV to control various smart home devices |
| Cloud Gaming (GeForce NOW/Xbox Cloud Gaming) | Ability to play console games (PC/XBOX/PlayStation) without a separate game console |
Smart features and additional functions of TVs vary greatly in usage depending on the individual, so we recommend checking and selecting the features you need.
While smart TV features like connecting to smartphones or accessing YouTube and Netflix are convenient, if you’re using IPTV with a set-top box, you can use basic functions even without smart features.
3. TV Power Consumption
Power consumption itself isn’t high, but it’s worth checking for long-term use
TVs are Among the Lower Power-Consuming Home Appliances

While TV power consumption isn’t particularly high, it can vary significantly depending on:
1) TV size
2) Panel/backlight method
Separately, TVs from smaller companies often have higher power consumption than those from major companies.
Chapter 4.
Additional Tips for TV
Lesser-Known Brand Products
1. Pros and Cons of Lesser-Known Brand Products
They’re indeed excellent in terms of cost-effectiveness,
but we recommend purchasing after fully considering the drawbacks
Outstanding Cost-Effectiveness is the Main Advantage
Many people consider TVs from lesser-known brands due to their low prices. Most of these products use panels manufactured by Samsung or LG, and their picture quality and design have improved significantly.
However, picture quality isn’t determined solely by panel performance, and aspects like contrast and brightness often don’t match up to TVs from major brands.
Drawbacks Exist in Picture Quality, Sound, Response Speed, and After-Sales Service
Other drawbacks include:
1) inadequate sound that doesn’t match the high-quality picture,
2) slow response when turning on the TV or changing channels, and
3) inconvenient after-sales service, leading to post-purchase regret according to some reviews.
Despite these drawbacks, if you’re not sensitive to picture quality or if cost-effectiveness is important to you, products from lesser-known brands can still be a good choice.
Additionally, many lesser-known brand TVs now come with Android 11 OS or Google TV, improving the slow response speed, so it’s worth considering these when making a purchase.







